In previous posts, I’ve talked a lot about deep learning.
- Why Deep Learning Has Received So Much Attention Lately
- Real-Time Object Recognition Using a Webcam and Deep Learning
- Limitations of Deep Learning
- How Do Neural Networks Make Predictions?
- Artificial Feedforward Neural Network With Backpropagation From Scratch
- And many others…
However, I have never actually explained, in a concise way, what deep learning is, so here we go.
Deep learning is a technique for teaching a computer how to make predictions based on a set of inputs.
Input Data —–> Deep Learning Algorithm (i.e. Process) —–> Output Data
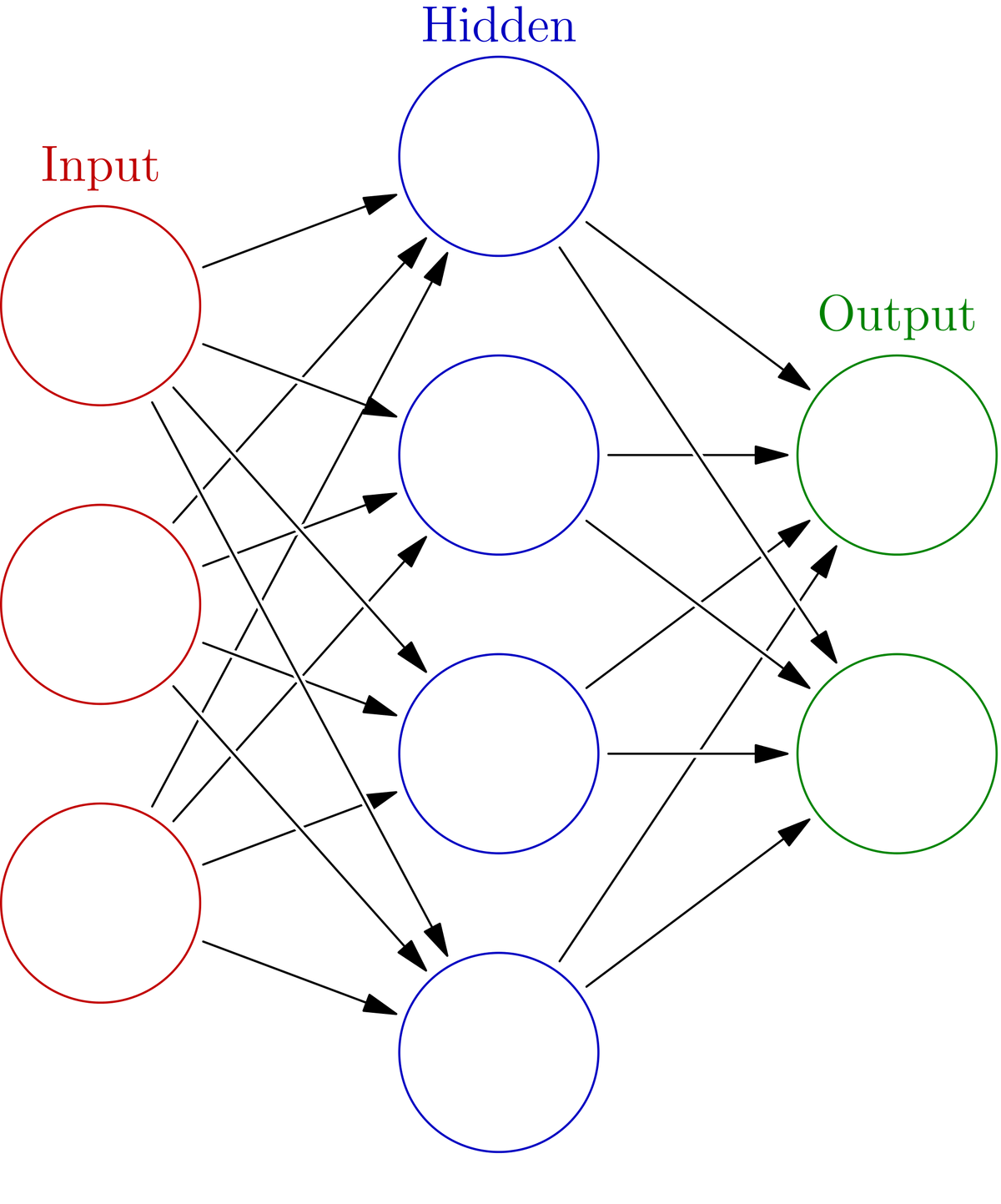
To make predictions (i.e. the “Process” part of the line above), deep learning uses deep neural networks. A deep neural network is a computer-based, simplified representation of neurons in the brain. It is computer science’s attempt to get a computer to process information just like real neurons in our brains do.
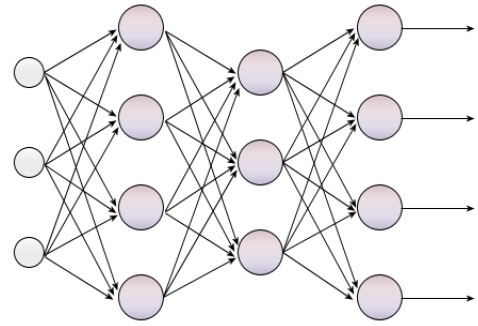
Deep neural networks are well suited for complex applications like computer vision, natural language processing, and machine translation where you want to draw useful information from nonlinear and unstructured data such as images, audio, or text.