In this project, we will get started on our Robot Operating System (ROS) programming journey by installing Ubuntu. Ubuntu is a popular distribution (i.e. flavor) of the Linux operating system and is fully supported by ROS, the most popular framework for writing robotics software. If you have a Windows PC (I have Windows 11), I recommend you install a VirtualBox first and then install Ubuntu in the Virtual Box. I’ll show you how to do all that below.
The process for installing Ubuntu has a lot of steps, so hold on tight, don’t give up if something goes wrong, and go slowly so that you get your installation setup properly. Let’s get started!
Requirements
Here are the project requirements:
- Install Ubuntu
- Install Virtual Box
- Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox
- Learn Important Linux Terminal Commands
You Will Need
The following components are used in this project. You will need:
- Windows PC that has the required processor, memory, and hard drive space
Directions
Download the Ubuntu Image
Check Ubuntu Releases to find the latest version of Ubuntu that has long term support (LTS). As of this writing, the latest release is Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (Jammy Jellyfish). You can download 22.04 if you want, but I will download Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa) since I need it for my ROS 2 Galactic work.
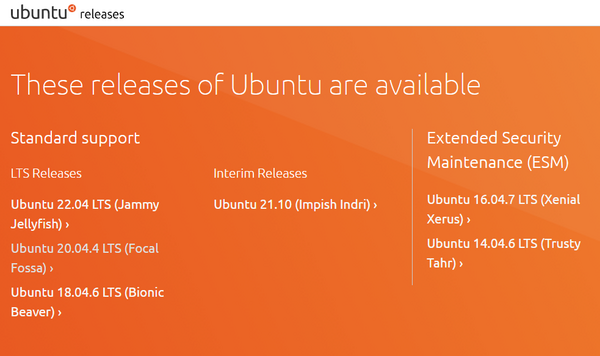
Click on the latest release of Ubuntu, and download the 64-bit PC (AMD64) desktop image (.iso file). The download process will take a while since it is a large file.
Before installing Ubuntu, you need to install Virtual Box. Virtual Box extends the capabilities of your host computer (i.e. your laptop or desktop PC) by enabling you to install and run an operating system in a new environment on top of your current operating system (Windows 11 in my case). The environment the new operating system will run in is known as a virtual machine (or guest).
Install VirtualBox
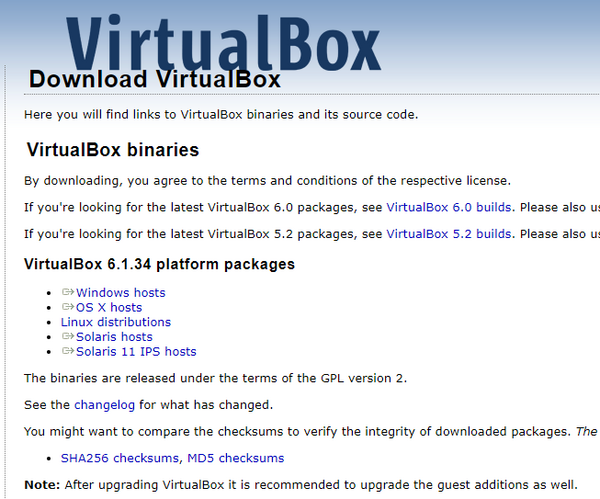
Let’s download VirtualBox. Go to VirtualBox downloads.
Select the platform package for Windows hosts to download the executable (.exe) file.
Detailed installation instructions for all operating systems (Windows, Mac OS, Linux, and Solaris) can be found in the instruction manual. Let’s go through the steps.
Double-click on the executable file.
Click Next to begin the installation process.
Click Next to install the VirtualBox in the default location.
Click Next to choose the default features.
You will see a warning about network interfaces. Ignore it, and click Yes to proceed.
You are now ready to install VirtualBox. Click Install to proceed.
Click Finish to run VirtualBox.
You can optionally delete the original executable file for VirtualBox (the one with the .exe extension). You don’t need it anymore.
Create a Virtual Machine
Now that VirtualBox is installed on your computer, we need to now create a new virtual machine.
Click the New button in the toolbar.
Type in a descriptive name for your operating system. You can stick with the default machine folder. The machine folder is where your virtual machines will be stored.
Also, select the operating system that you want to later install (Linux in this case).
Click Next to proceed.
The default memory size for me is 1024 MB. That is not enough. Raise it to 6470 MB, and then click Next to proceed.
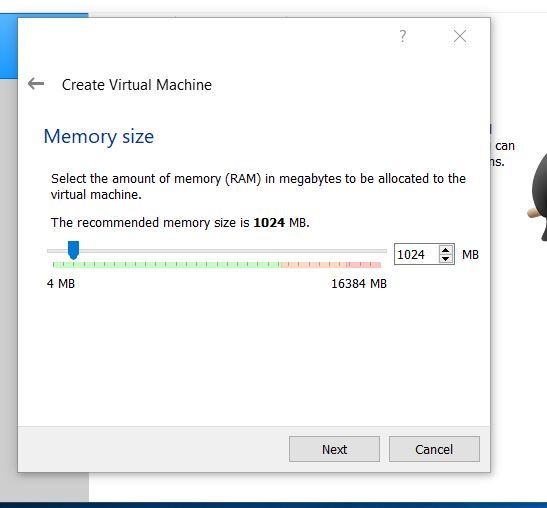
Make sure “Create a virtual hard disk now” is selected, and click Create.
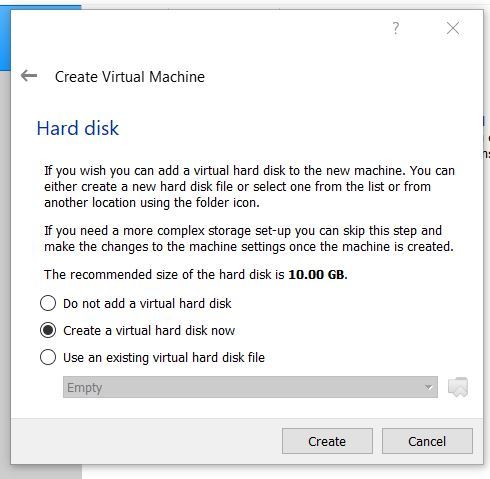
Select “VirtualBox Disk Image (VDI)”, and click Next.
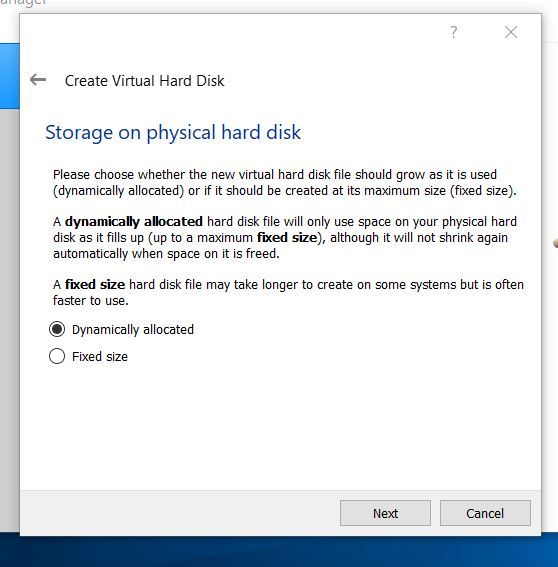
Choose a Fixed size virtual hard disk so that you have better performance, and click next.
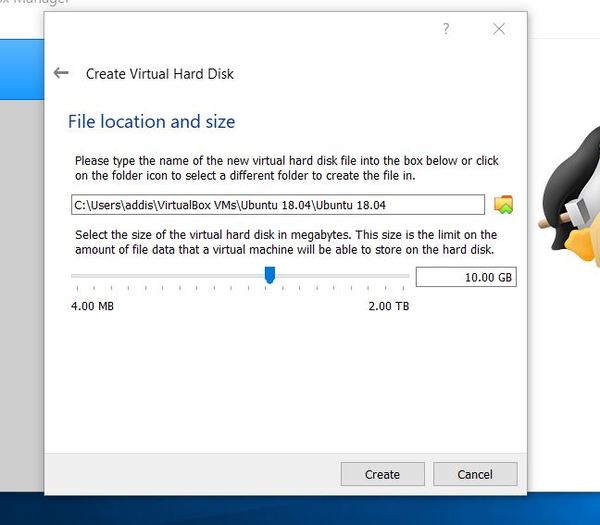
You can stick with the default hard disk space (10GB as of the time of this writing) or go with something like 50 GB. I went with 50 GB. I also prefer to save my hard disk on my D drive (which has more space than my C drive). Then click Create.
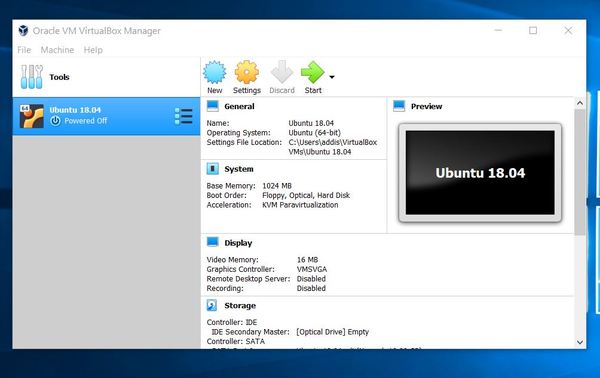
Double-click on the left panel where it says “Ubuntu 18.04.” A startup window will appear.
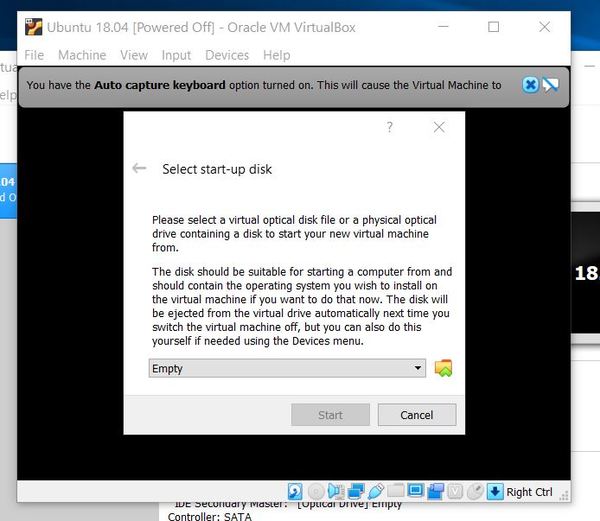
Click the Folder icon next to Empty and select the Ubuntu image you downloaded earlier in this tutorial. It is a .iso file. You can make sure that your .iso file is somewhere in your C drive (doesn’t have to be on your Desktop). Then click Start to proceed.
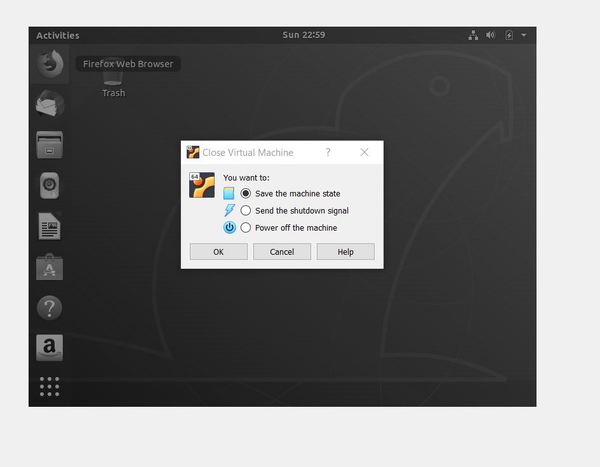
You might get an error that looks like this.
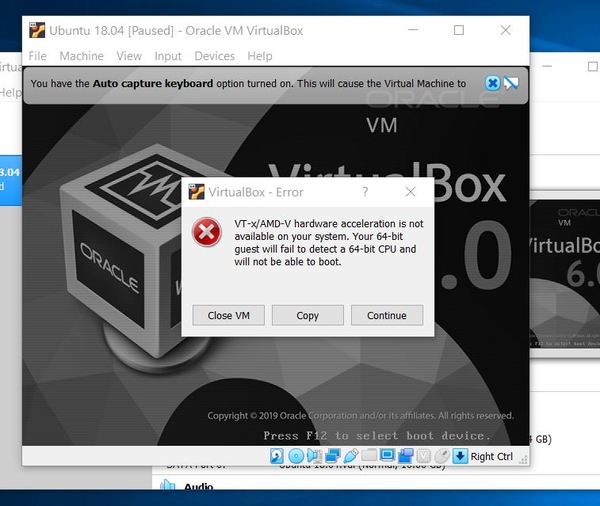
Click Close VM.
Enable Virtualization Technology on Your Computer
The error above arises because virtualization technology is disabled on your computer by default. We need to enable it. Let’s do that now.
Go down to the search area on your computer in the bottom left of your screen, and searched for “Advanced Startup”.
Click “Change Advanced Startup Options.”
Click Restart Now.
Click Troubleshoot.
Click Advanced Options.
Click UEFI Firmware Settings.
Click Restart to change the UEFI Firmware Settings.
Click F10 BIOS Setup.
Press the right arrow to go to System Configuration.
Scroll down to Virtualization Technology.
Press Enter to select Enabled.
Press the down arrow and then Enter to select Enabled.
Press F10 to save and exit.
Press Enter on Yes to save the changes.
Your computer will reboot.
Double-click on the VirtualBox icon to start it.
Click on the left panel of the window to start the Ubuntu virtual machine. Or you can just click Start in the toolbar.
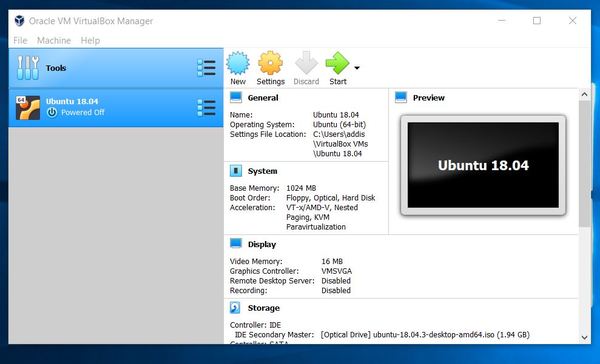
You should see the Ubuntu window appear.
Install Ubuntu
Click on “Install Ubuntu” to install Ubuntu.
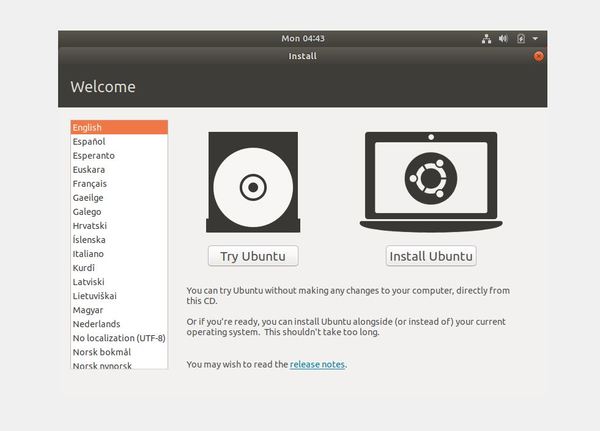
Click “Continue” to save the keyboard layout. The default English one is fine.
Keep clicking Continue through all the prompts. The options you want selected as you go through the prompts are the following:
- Download updates while installing Ubuntu
- Erase disk and install Ubuntu
You will get to a point where you will need to set your time zone. It will be a big map of the world that should automatically detect your location.
Type in a computer name and pick a username and password. I select the “Log in automatically” option.
When installation is complete, click “Restart Now.”
If you get a message that says “Please remove the installation medium. Then press ENTER,” just press ENTER.
When you reboot, you will go to the Ubuntu desktop.
If at any time you want to exit Ubuntu, go to File → Close. You will be given the option to save your machine state so that you can pick up where you left off the next time you login to Ubuntu.
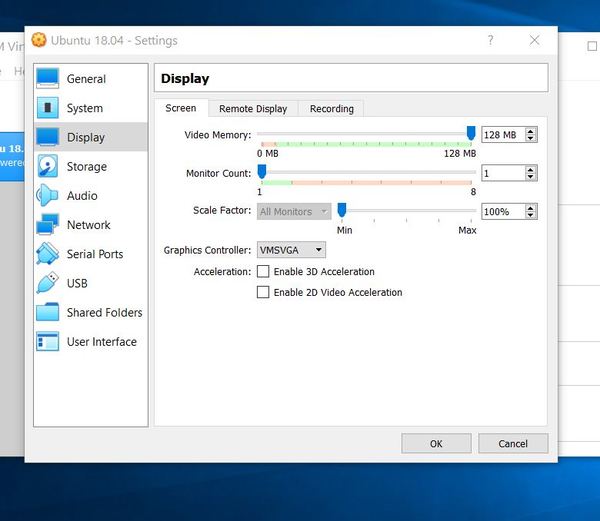
Two additional notes….when you power up your VirtualBox, it is a good idea to go to Settings → Display and change your Video Memory to 128 MB. This will give you ample video memory.
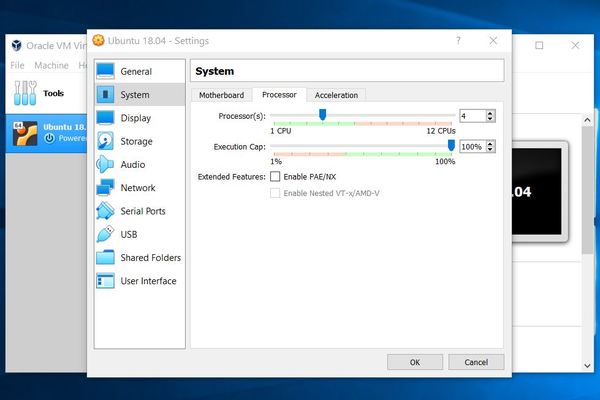
Also go to Settings → System → Processor, and adjust the number of CPUs to 4.
If you at any point in the future run out of hard drive space for your virtual machine, you can move it to another drive (e.g. D drive) by following this article at Tech Republic.
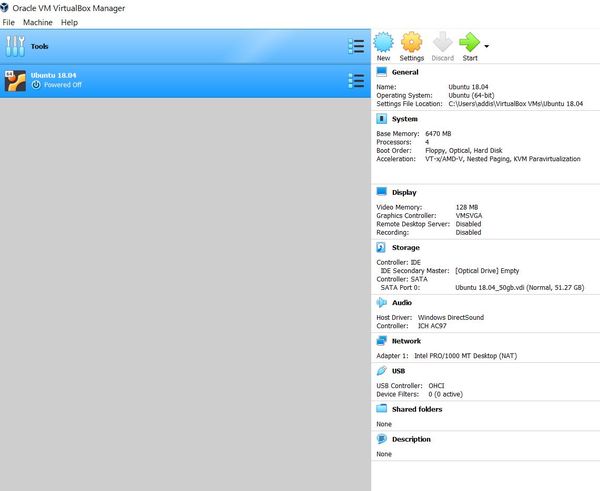
Here are the complete settings on my Windows machine.
Getting Used to Ubuntu
Similar to the C drive in Windows 10, Linux has a file system (everything branches from the / symbol). You can find it by clicking the icon of the file cabinet on the right side of the desktop. It is the third icon down in the image below.
Click “Other Locations.”
Click “Computer.”
You will see all the files. For example, the path to the bin file is /bin
You can find popular software applications for download in the Ubuntu Software module. It is the sixth icon in the left-hand panel.

Linux Terminal Commands With the Ubuntu Command-Line Interface
We could certainly navigate around Ubuntu using the graphical user interface, but we would miss out on being able to run advanced processes for ROS. This is where the Terminal application comes in handy. The Terminal application is the Ubuntu command-line interface and is similar to the Command Prompt on a Windows 10 system. It enables us to use Linux terminal commands.
To open the Terminal, click the bottom left where you see those nine white dots and search for “Terminal” at the top.
Click on Terminal.
If you do a Google search for “common Linux terminal commands,” you should find some nice cheat sheets to use as a reference. Let’s try a few common commands below.
The following command retrieves a list of all the files and folders in the current directory.
ls
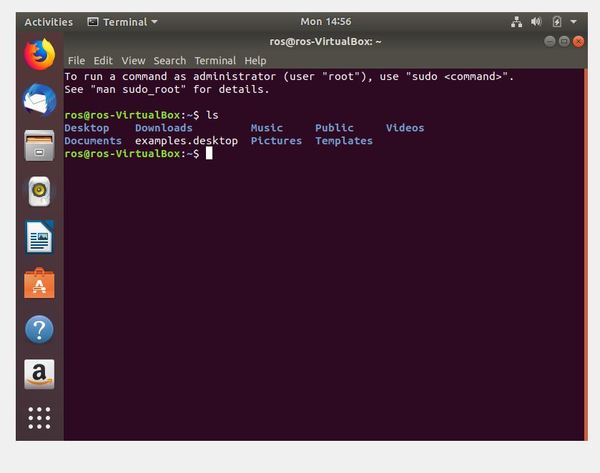
If you want to change to the desktop, type:
cd Desktop
If you want to get the path to the current directory, type:
pwd
To go up one directory, type:
cd ~
To update the list of packages, type:
sudo apt-get update
The sudo keyword enables you to run a command as an administrator.
At this stage, it would be useful for you to install htop, an interactive system-monitor process-viewer and process-manager. To install it, type the following command:
sudo apt-get install htop
If at any point you want to remove it, you can type the following command:
sudo apt-get remove htop
To run, htop, you type:
htop
You can reboot the system using the following command:
sudo reboot
Finally, to shutdown the system, you type the following command:
sudo poweroff