In this tutorial, we will learn how to create a finite state machine using the SMACH Python-based library and ROS.
Real-World Applications
In the context of robotics, a finite state machine consists of states (e.g. robot is OFF, robot is moving, robot is charging, etc.), an initial state, and inputs that can cause the robot system to change from one state to another state.
Prerequisites
- You have ROS running on Ubuntu Linux
- I am using ROS Noetic.
- I’m running my Ubuntu Linux inside a virtual machine on Windows 10. If you have MacOS or Linux, that will work just fine. Just make sure you have ROS installed.
Finite State Machine Example

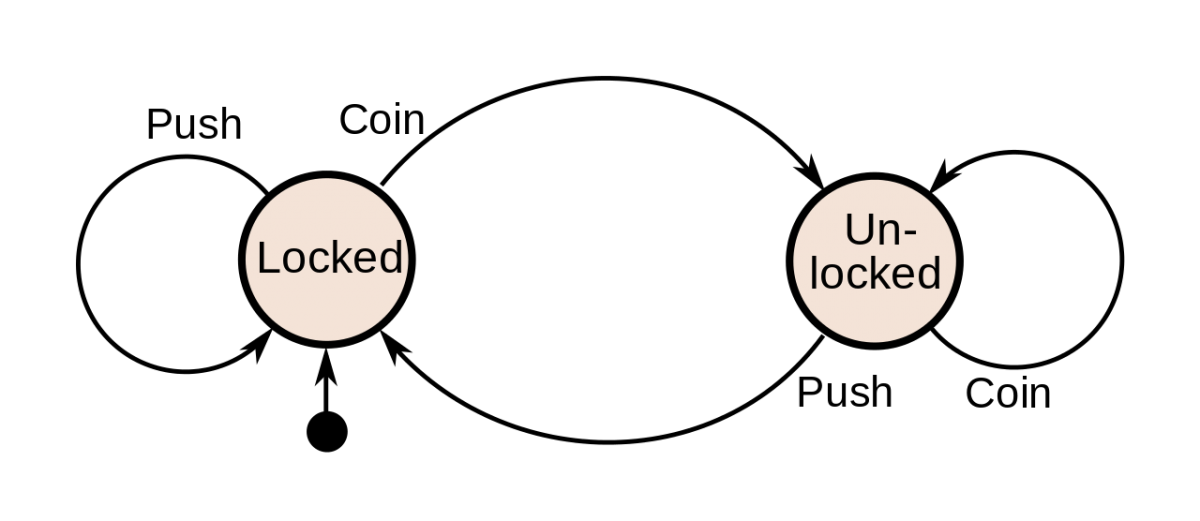
A turnstile at a metro station or a stadium is an example of a mechanism that can be modeled using a finite state machine. In the case of a turnstile, we have the following finite state machine:
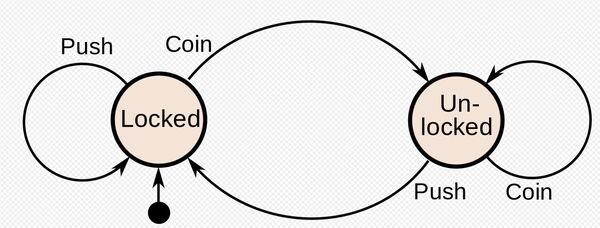

You will notice that there are two states: locked and unlocked. There are two inputs that can cause the current state to transition from one state to another: coin (i.e. customer inserts coin) and push (i.e. customer pushes the turnstile).
In the locked state, when the customer inserts a coin, the turnstile transitions to unlocked. However, if the customer pushes the turnstile without inserting a coin, the turnstile remains locked.
In the unlocked state, when the customer inserts a coin, the turnstile remains in the unlocked state. If the customer pushes the turnstile in the unlocked state, the turnstile let’s the customer through, and then it transitions to the locked state.
Getting Started
To create finite state machines in ROS, we use the Python library called SMACH (you pronounce this as “smash”).
Let’s begin by installing the required software.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-smach ros-noetic-smach-ros ros-noetic-executive-smach
Create a ROS Package
Let’s create a ROS package.
In a new terminal window, move to the src (source) folder of your workspace.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
Now create the package.
catkin_create_pkg turnstile_smach std_msgs roscpp rospy
cd ~/catkin_ws/
catkin_make --only-pkg-with-deps turnstile_smach
Write the Code
Move to your package by opening a new terminal window, and typing:
roscd turnstile_smach
Create a new folder called scripts.
mkdir scripts
Move inside that folder.
cd scripts
Create a new script.
gedit fsm_turnstile.py
Add the following code inside the script.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Author: Automatic Addison https://automaticaddison.com
# Description: An example of a basic finite state machine for a turnstile at
# a stadium or metro station.
# Import the necessary libraries
import rospy # Python client library
from smach import State, StateMachine # State machine library
import smach_ros # Extensions for SMACH library to integrate it with ROS
from time import sleep # Handle time
# Define state LOCKED
class Locked(State):
def __init__(self):
State.__init__(self, outcomes=['push','coin'], input_keys=['input'])
# Inside this block, you can execute any code you want
def execute(self, userdata):
sleep(1)
rospy.loginfo('Executing state LOCKED')
# When a state finishes, an outcome is returned. An outcome is a
# user-defined string that describes how a state finishes.
# The transition to the next state is based on this outcome
if userdata.input == 1:
return 'push'
else:
return 'coin'
# Define state UNLOCKED
class Unlocked(State):
def __init__(self):
State.__init__(self, outcomes=['push','coin'], input_keys=['input'])
def execute(self, userdata):
sleep(1)
rospy.loginfo('Executing state UNLOCKED')
if userdata.input == 1:
return 'push'
else:
return 'coin'
# Main method
def main():
# Initialize the node
rospy.init_node('fsm_turnstile_py')
# Create a SMACH state machine container
sm = StateMachine(outcomes=['succeeded','failed'])
# Set user data for the finite state machine
sm.userdata.sm_input = 0
#sm.userdata.sm_input = input("Enter 1 to Push or 0 to Insert a Coin: ")
# Open the state machine container. A state machine container holds a number of states.
with sm:
# Add states to the container, and specify the transitions between states
# For example, if the outcome of state LOCKED is 'coin', then we transition to state UNLOCKED.
StateMachine.add('LOCKED', Locked(), transitions={'push':'LOCKED','coin':'UNLOCKED'}, remapping={'input':'sm_input'})
StateMachine.add('UNLOCKED', Unlocked(), transitions={'push':'LOCKED','coin':'UNLOCKED'}, remapping={'input':'sm_input'})
# View our state transitions using ROS by creating and starting the instrospection server
sis = smach_ros.IntrospectionServer('server_name', sm, '/SM_ROOT')
sis.start()
# Execute the state machine
outcome = sm.execute()
# Wait for ctrl-c to stop the application
rospy.spin()
sis.stop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Save the file, and close it.
Change the permissions of the file.
chmod +x fsm_turnstile.py
Open a new terminal window, and type:
cd ~/catkin_ws/
Build the package.
catkin_make --only-pkg-with-deps turnstile_smach
Run the Code
Open a new terminal window, and type:
cd ~/catkin_ws/
Start ROS.
roscore
Open a new terminal, and launch the finite state machine Python file you created.
rosrun turnstile_smach fsm_turnstyle.py
Here is the output:
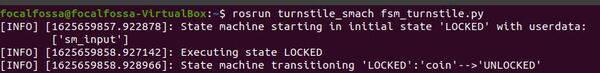
If you want to change the output, you can change the code so that the state machine input is 1 (i.e. push).
sm.userdata.sm_input = 1Note that the SMACH viewer is unmaintained and doesn’t work with ROS Noetic.
That’s it! Keep building!
For a more in-depth look at SMACH with ROS, check out the official tutorials.