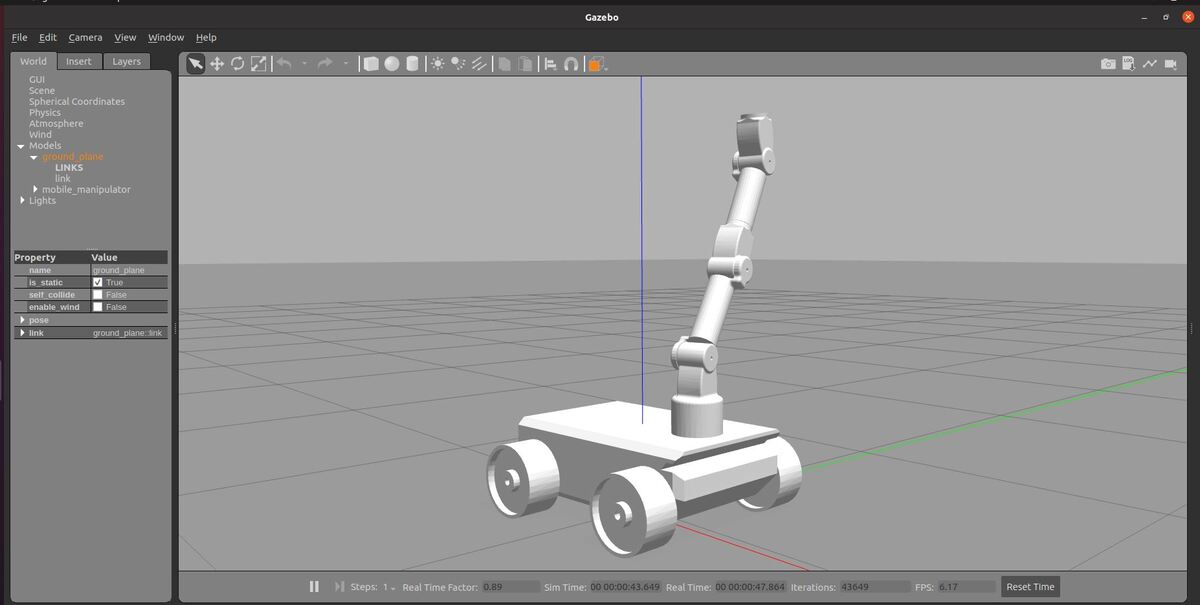
In this tutorial, we will create a mobile manipulator using a wheeled robot base and a robotic arm. All we need to do is to connect the arm_base link of the robot arm to the base_link of the robot.
This tutorial would not have been possible without Ramkumar Gandhinathan and Lentin Joseph’s awesome book ROS Robotics Projects Second Edition (Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases). I highly recommend it if you want to learn ROS 1. Many of the files (URDF, configuration, and STL files), come from their book’s public GitHub page.
Real-World Applications
This project has a number of real-world applications:
- Indoor Delivery Robots
- Order Fulfillment
- Factories
- Warehouses
- Space Exploration
- Power Plants
Let’s get started!
Prerequisites
- You have completed this tutorial where you learned how to create a mobile robot base.
- You have completed this tutorial where you learned how to create a robotic arm.
Build the Mobile Manipulator
Open a new terminal window.
Move to the urdf folder of your package.
roscd mobile_manipulator_body/urdf/
Now create a file named mobile_manipulator.urdf.
gedit mobile_manipulator.urdf
Add the mobile_manipulator.urdf code inside there.
Save and close the file.
Test the Mobile Manipulator
Now, let’s launch RViz to see what our robot looks like so far.
roscd mobile_manipulator_body/urdf/
roslaunch urdf_tutorial display.launch model:=mobile_manipulator.urdf
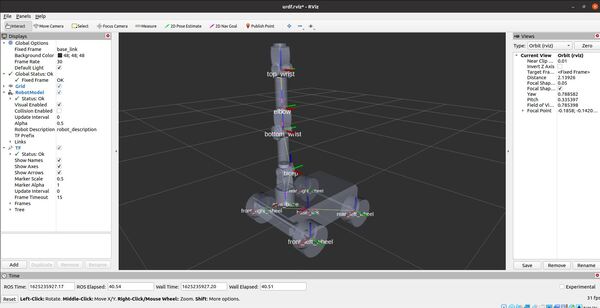
A GUI will appear that will enable you to move the joints.
Launch the Mobile Manipulator
Now let’s launch the mobile manipulator.
Open a new terminal window, and go to the package.
roscd mobile_manipulator_body/launch/
Create a new launch file.
gedit mobile_manipulator_gazebo.launch
Add the mobile_manipulator_gazebo.launch code inside there.
Save and close the file.
Now let’s launch the robot in Gazebo.
Move to your catkin workspace.
cd ~/catkin_ws/
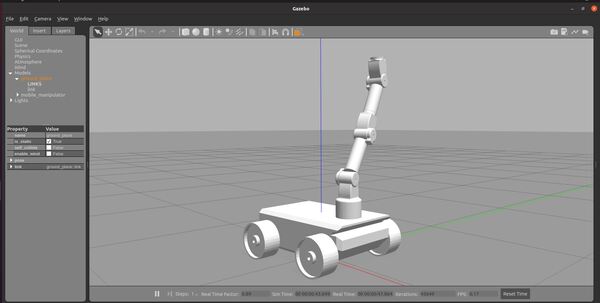
roslaunch mobile_manipulator_body mobile_manipulator_gazebo.launch
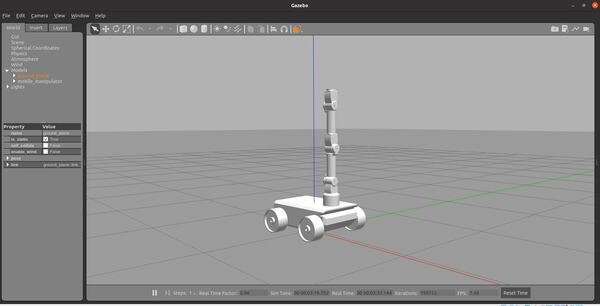
Here is how the robot looks.
Here are the active ROS topics.
rostopic list
Open a new terminal, and type this command to move the robot arm a little bit:
rostopic pub /arm_controller/command trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectory '{joint_names: ["arm_base_joint","shoulder_joint", "bottom_wrist_joint", "elbow_joint","top_wrist_joint"], points: [{positions: [-0.1, 0.5, 0.02, 0, 0], time_from_start: [1,0]}]}' -1
Type this command to bring the robot back to the home position.
rostopic pub /arm_controller/command trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectory '{joint_names: ["arm_base_joint","shoulder_joint", "bottom_wrist_joint", "elbow_joint","top_wrist_joint"], points: [{positions: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0], time_from_start: [1,0]}]}' -1
You can steer the robot by opening a new window and typing:
rosrun rqt_robot_steering rqt_robot_steering
You will need to change the topic inside the GUI to:
/robot_base_velocity_controller/cmd_vel
To see the velocity messages, open a new window and type:
rostopic echo /robot_base_velocity_controller/cmd_vel