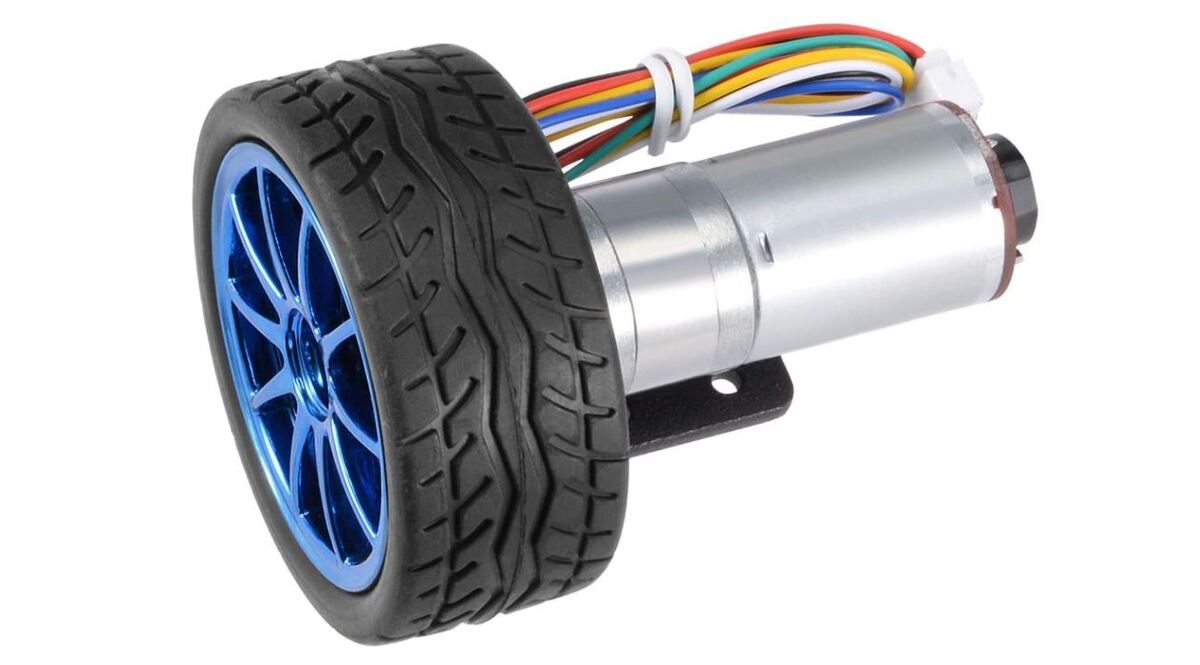
In this tutorial, we learn how to calculate the angular velocity (magnitude and direction of rotation in radians per second) of a DC motor with a built-in encoder.
Here is the motor we will work with, but you can use any motor that looks like this one.

Real-World Applications
Knowing the angular velocity of wheels on a robot helps us calculate how fast the robot is moving (i.e. speed) as well as the distance a robot has traveled in a given unit of time. This information is important for helping us determine where a robot is in a particular environment (i.e. odometry).
Prerequisites
- You have the Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment) installed on your PC (Windows, MacOS, or Linux).
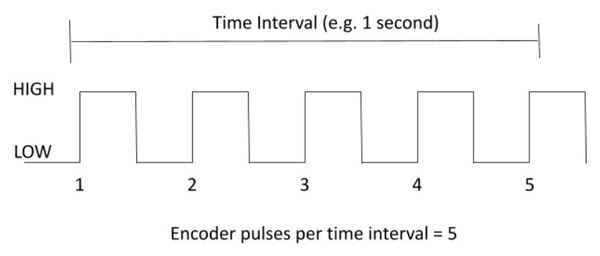
- You know how to calculate the number of pulses per revolution for a DC motor with a built-in encoder.
You Will Need
This section is the complete list of components you will need for this project (#ad).
2 x JGB37-520B DC Motor with Encoder OR 2 x JGB37-520B DC 6V 12V Micro Geared Motor With Encoder and Wheel Kit (includes wheels)
OR
Self-Balancing Car Kit (which includes everything above and more…Elegoo and Osoyoo are good brands you can find on Amazon.com)
Disclosure (#ad): As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Set Up the Hardware
The first thing we need to do is set up the hardware.
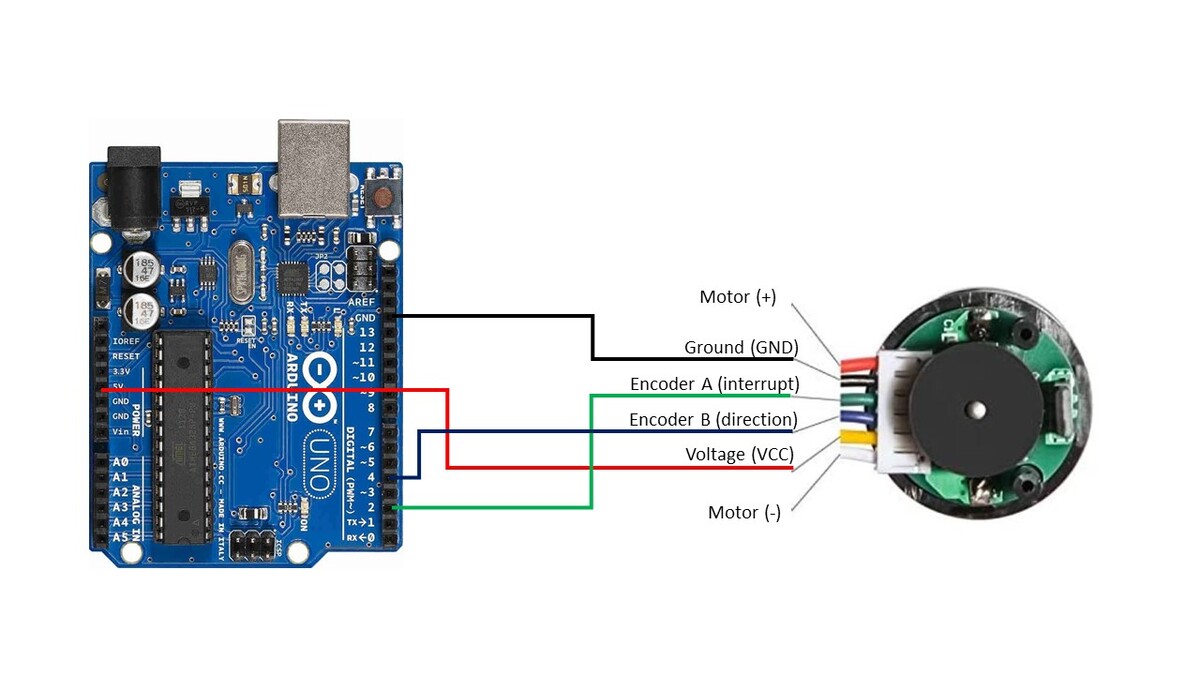
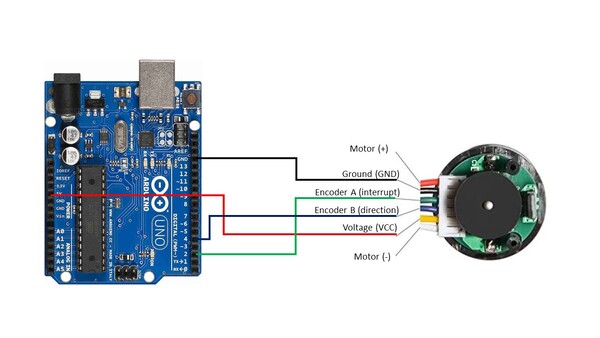
Here is the wiring diagram:
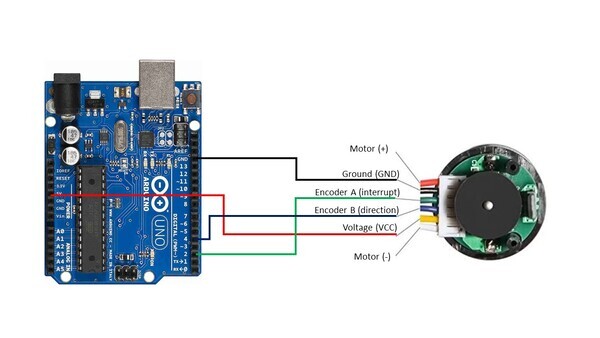
- The Ground pin of the motor connects to GND of the Arduino.
- Encoder A (sometimes labeled C1) of the motor connects to pin 2 of the Arduino. Pin 2 of the Arduino will record every time there is a rising digital signal from Encoder A.
- Encoder B (sometimes labeled C2) of the motor connects to pin 4 of the Arduino. The signal that is read off pin 4 on the Arduino will determine if the motor is moving forward or in reverse.
- The VCC pin of the motor connects to the 5V pin of the Arduino. This pin is responsible for providing power to the encoder.
- For this project, you don’t need to connect the motor pins (+ and – terminals) to anything since you will be turning the motor manually with your hand.
Write and Load the Code to Calculate Angular Velocity
Now we’re ready to calculate the angular velocity of the wheel.
Open the Arduino IDE, and write the following program. The name of my program is calculate_angular_velocity.ino.
/*
* Author: Automatic Addison
* Website: https://automaticaddison.com
* Description: Calculate the angular velocity in radians/second of a DC motor
* with a built-in encoder (forward = positive; reverse = negative)
*/
// Motor encoder output pulses per 360 degree revolution (measured manually)
#define ENC_COUNT_REV 620
// Encoder output to Arduino Interrupt pin. Tracks the pulse count.
#define ENC_IN_RIGHT_A 2
// Other encoder output to Arduino to keep track of wheel direction
// Tracks the direction of rotation.
#define ENC_IN_RIGHT_B 4
// True = Forward; False = Reverse
boolean Direction_right = true;
// Keep track of the number of right wheel pulses
volatile long right_wheel_pulse_count = 0;
// One-second interval for measurements
int interval = 1000;
// Counters for milliseconds during interval
long previousMillis = 0;
long currentMillis = 0;
// Variable for RPM measuerment
float rpm_right = 0;
// Variable for angular velocity measurement
float ang_velocity_right = 0;
float ang_velocity_right_deg = 0;
const float rpm_to_radians = 0.10471975512;
const float rad_to_deg = 57.29578;
void setup() {
// Open the serial port at 9600 bps
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set pin states of the encoder
pinMode(ENC_IN_RIGHT_A , INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(ENC_IN_RIGHT_B , INPUT);
// Every time the pin goes high, this is a pulse
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(ENC_IN_RIGHT_A), right_wheel_pulse, RISING);
}
void loop() {
// Record the time
currentMillis = millis();
// If one second has passed, print the number of pulses
if (currentMillis - previousMillis > interval) {
previousMillis = currentMillis;
// Calculate revolutions per minute
rpm_right = (float)(right_wheel_pulse_count * 60 / ENC_COUNT_REV);
ang_velocity_right = rpm_right * rpm_to_radians;
ang_velocity_right_deg = ang_velocity_right * rad_to_deg;
Serial.print(" Pulses: ");
Serial.println(right_wheel_pulse_count);
Serial.print(" Speed: ");
Serial.print(rpm_right);
Serial.println(" RPM");
Serial.print(" Angular Velocity: ");
Serial.print(rpm_right);
Serial.print(" rad per second");
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(ang_velocity_right_deg);
Serial.println(" deg per second");
Serial.println();
right_wheel_pulse_count = 0;
}
}
// Increment the number of pulses by 1
void right_wheel_pulse() {
// Read the value for the encoder for the right wheel
int val = digitalRead(ENC_IN_RIGHT_B);
if(val == LOW) {
Direction_right = false; // Reverse
}
else {
Direction_right = true; // Forward
}
if (Direction_right) {
right_wheel_pulse_count++;
}
else {
right_wheel_pulse_count--;
}
}
Compile the code by clicking the green checkmark in the upper-left of the IDE window.
Connect the Arduino board to your personal computer using the USB cord.
Load the code we just wrote to your Arduino board.
Open the Serial Monitor.
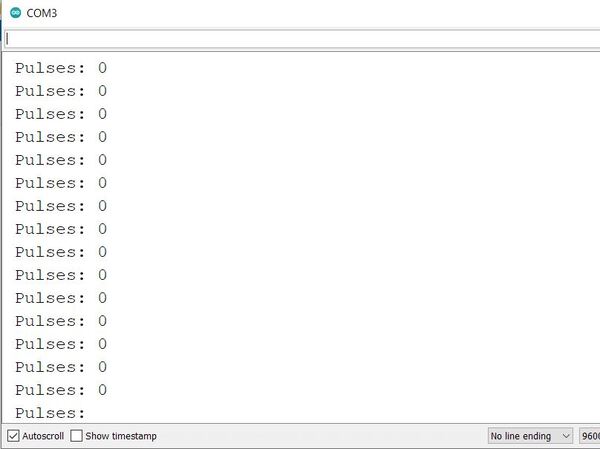
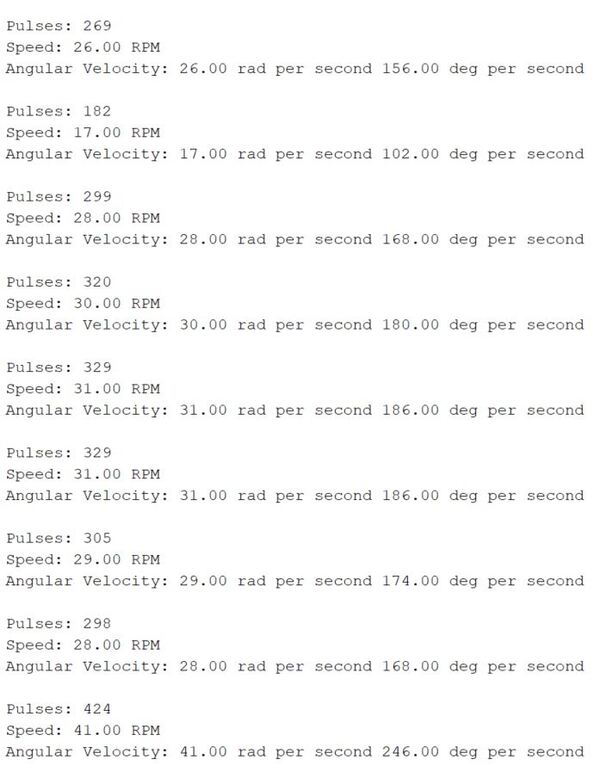
Here is the output when I rotate the motor forward:
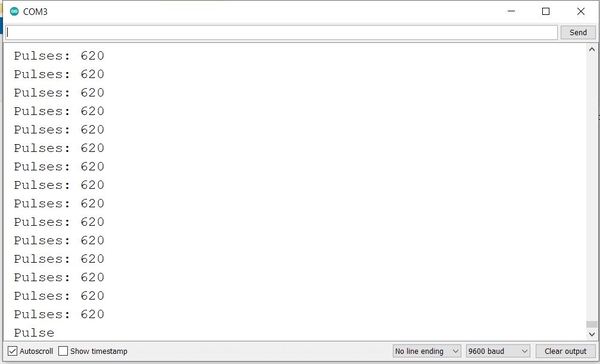
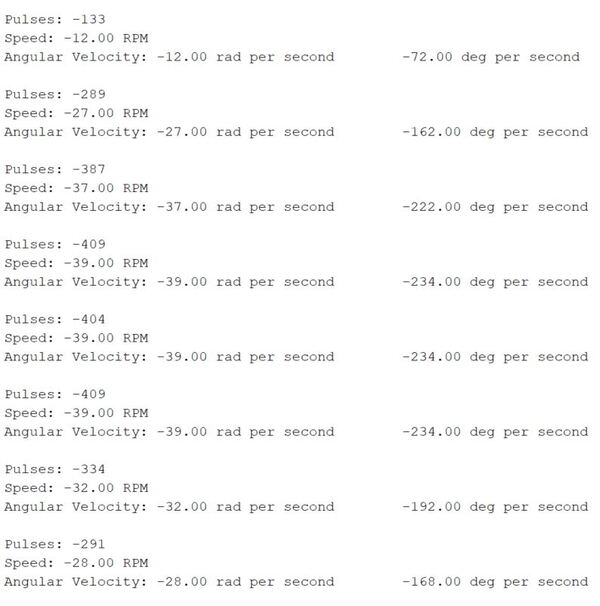
Here is the output when I rotate the motor in reverse.
Calculating Linear Velocity
Now that you know how to calculate the angular velocity of a wheel, you can calculate the linear velocity of that wheel if you know it’s radius. Here is the equation:
(Linear Velocity in meters per second) = (Radius of the wheel in meters) * (Angular Velocity in radians per second)
This equation above is commonly written as:
v = r * ω
That’s it. Keep building!