In this post, I will write example code for the most common things you’ll do in MATLAB. MATLAB is a software package used for numerical computation and visualization.
My goal is to write bare-bones, skeleton recipes that can be easily modified and adapted to your own projects.
Prerequisites
- You have MATLAB installed on your computer. I’m using MATLAB Release 2020a.
Select a Current Directory
Open MATLAB.
In the command window, select your desired Current Folder (i.e. working directory). The syntax is:
cd 'path_to_folder'
For example., in the Command Window, you would type the following command and press Enter in your keyboard:
cd 'C:\Program Files\My_Documents'
Create New Scripts
To create a new script (i.e. the most basic Matlab file with the ‘.m’ extension), run the following command in the Command window.
edit matlab_cookbook_1.m
If this is your first time creating a file in MATLAB, you might see a prompt that asks you “Do you want to create it?”
Highlight “Do not show this prompt again,” and click Yes.
Accept User Input
Write the following code inside matlab_cookbook_1.m.
% Get rid of blank lines in the output
format compact
% Accept a string as input
% Semicolon prevents every variable and output from appearing
% in the command window
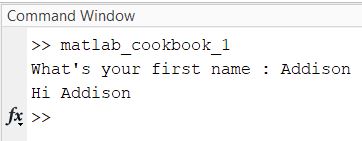
name = input("What's your first name : ", "s");
% Check if the user entered something as input
if ~isempty(name)
fprintf("Hi %s\n", name)
end
Save the code.
Click Run to run the code.
Type in your name into the Command Window.
Press Enter.
Here is the output:
To stop a script from running at any time, you can type CTRL+C.
Now, let’s create a new file named matlab_cookbook_2.m.
edit matlab_cookbook_2.m
Add the following code:
% Get rid of blank lines in the output
format compact
% Accept vector input
vector_input = input("Enter a vector : ");
% Display the vector to the Command Window
disp(vector_input)
Click Run.
Enter your vector. For example, you can enter:
[1 2 3]
Here is the output:

Declare and Initialize Variables and Data Types
Let’s work with variables and data types (i.e. classes).
Create a new script.
edit matlab_cookbook_3.m
Type the following code.
format compact
% Initialize a character variable
char_1 = 'A'
% Determine the class of a character
class(char_1)
% Initialize a string variable
str_1 = "This is a string"
% Determine the class
class(str_1)
% Evaluate a boolean expression
5 > 2
% Initialize a boolean varable to true
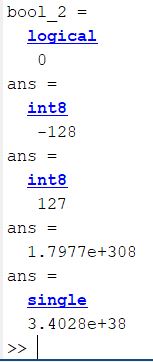
bool_1 = true
% Initialize a boolean variable to false
bool_2 = false
% Check out the maximum and minimum values that can be
% stored in a data type
intmin('int8')
intmax('int8')
% See the largest double value that can be stored
realmax
% See the largest integer that can be stored
realmax('single')
Run it.
Here is the output:

How do you create an expression that spans more than one line?
Open a new script.
edit matlab_cookbook_4.m
format compact
% An expression that spans more than one line
var_1 = 5 + 5 + 1 ...
+ 1
Save and then run the code.
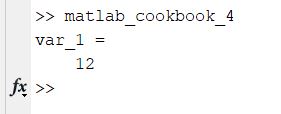
Casting Variables to Different Data Types
Let’s explore how to cast variables to different data types.
Create a new script.
edit matlab_cookbook_5.m
Type the following code.
format compact
% Create a double (double is the default)
var_1 = 9
% Output the data type
class(var_1)
% Caste the double to an int8 data type
var_2 = int8(var_1)
% Check that the variable was properly converted
class(var_2)
% Convert a character to a double
var_3 = double('A')
% Convert a double to a character
var_4 = char(64)
Run it.
Here is the output:

Formatting Data into a String
Let’s explore how to format data into a string.
Create a new script.
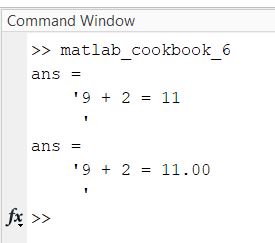
edit matlab_cookbook_6.m
Type the following code.
format compact
% Format output into a string.
% Sum should be a signed integer - %d
sprintf('9 + 2 = %d\n', 9 + 2)
% Format output into a string.
% Sum should be a float with two decimal places
sprintf('9 + 2 = %.2f\n', 9 + 2)
Run it.
Here is the output:
Basic Mathematical Operations
Let’s explore how to do basic mathematical operations in MATLAB.
Create a new script.
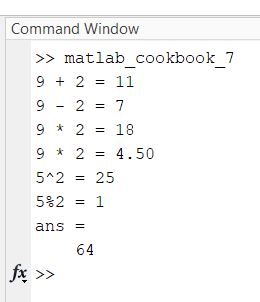
edit matlab_cookbook_7.m
Type the following code.
% Supress the display of blank lines
format compact
% Display formatted text
% Addition
fprintf('9 + 2 = %d\n', 9 + 2)
% Subtraction
fprintf('9 - 2 = %d\n', 9 - 2)
% Multiplication
fprintf('9 * 2 = %d\n', 9 * 2)
% Display float with two decimal places
fprintf('9 * 2 = %0.2f\n', 9 / 2)
% Exponentiation
fprintf('5^2 = %d\n', 5^2)
% Modulus
fprintf('5%%2 = %d\n', mod(5,2))
% Generate a random number between 50 and 100
randi([50,100])
Run it.
Here is the output:
Basic Mathematical Functions
Let’s take a look at some basic mathematical functions in MATLAB.
Create a new script.
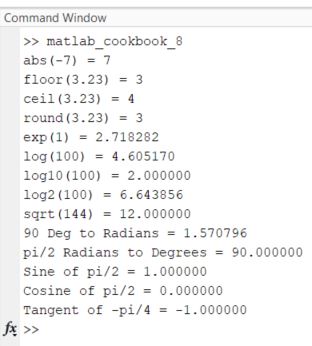
edit matlab_cookbook_8.m
Type the following code.
format compact
% This code has some basics mathematical functions
% in MATLAB
% Absolute Value
fprintf('abs(-7) = %d\n', abs(-7))
% Floor
fprintf('floor(3.23) = %d\n', floor(3.23))
% Ceiling
fprintf('ceil(3.23) = %d\n', ceil(3.23))
% Rounding
fprintf('round(3.23) = %d\n', round(3.23))
% Exponential (e^x)
fprintf('exp(1) = %f\n', exp(1))
% Logarithms
fprintf('log(100) = %f\n', log(100))
fprintf('log10(100) = %f\n', log10(100))
fprintf('log2(100) = %f\n', log2(100))
% Square root
fprintf('sqrt(144) = %f\n', sqrt(144))
% Convert from degrees to radians
fprintf('90 Deg to Radians = %f\n', deg2rad(90))
% Convert from radians to degrees
fprintf('pi/2 Radians to Degrees = %f\n', rad2deg(pi/2))
%%%% Trigonometric functions%%%
% Sine of argument in radians
fprintf('Sine of pi/2 = %f\n', sin(pi/2))
% Cosine of argument in radians
fprintf('Cosine of pi/2 = %f\n', cos(pi/2))
% Tangent of argument in radians
fprintf('Tangent of -pi/4 = %f\n', tan(-pi/4))
Run it.
Here is the output:
To see a big list of the built-in mathematical functions, you can type the following command:
help elfun
Relational and Logical Operators
Create a new script.
edit matlab_cookbook_9.m
Type the following code.
format compact
%{
Relational Operators:
-- Greater than >
-- Less than <
-- Greater than or equal to >=
-- Less than or equal to <=
-- Equal to ==
-- Not equal to ~=
Logical Operators:
-- OR ||
-- AND &&
-- NOT ~
%}
% Example
age = 19
if age < 18
disp("You are not in college yet")
elseif age >= 18 && age <= 22
disp("You are a college student")
else
disp("You have graduated from college")
end
Run it.
Here is the output:

Now, let’s work with switch statements.
edit matlab_cookbook_10.m
Here is the output:
format compact
size = 12
switch size
case 2
disp("Too small")
case num2cell(3:10) % If number is between 3 and 10, inclusive
disp("Just right")
case {11, 12, 13, 14} % If number is any of these numbers
disp("A bit large")
otherwise
disp("Too big")
end
Vectors
edit matlab_cookbook_11.m
Here is the output:
format compact
% Create a vector
vector_1 = [6 9 1 3 8]
% Calculate the length of the vector
vector_1_length = length(vector_1)
% Sort a vector in ascending order
vector_1 = sort(vector_1)
% Sort a vector in descending order
vector_1 = sort(vector_1, 'descend')
% Create a vector that has the numbers 3 through 9
vector_2 = 3:9
% Create a vector of numbers from 10 through 15 in steps of 0.5
vector_3 = 10:0.5:15
% Concatenate vectors
vector_4 = [vector_2 vector_3]
% Get the first item in the vector above. Indices start at 1.
vector_4(1)
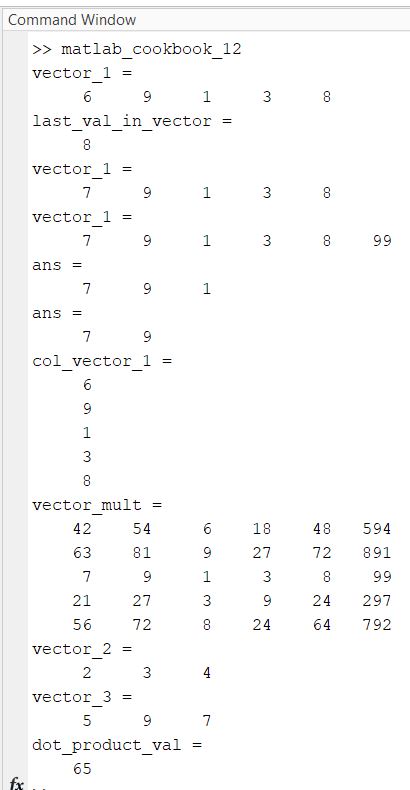
edit matlab_cookbook_12.m
format compact
% Create a vector
vector_1 = [6 9 1 3 8]
% Get the last value in a vector
last_val_in_vector = vector_1(end)
% Change the first value in a vector
vector_1(1) = 7
% Append values to end of vector
vector_1(6) = 99
% Get the first 3 values of a vector
vector_1(1:3)
% Get the first and second value of a vector
vector_1([1 2])
% Create a column vector
col_vector_1 = [6;9;1;3;8]
% Multiply a column vector and a row vector
vector_mult = col_vector_1 * vector_1
% Take the dot product of two vectors
% 2 * 5 + 3 * 9 + 4 * 7 = 65
vector_2 = [2 3 4]
vector_3 = [5 9 7]
dot_product_val = dot(vector_2, vector_3)
Here is the output:
Matrix Basics
edit matlab_cookbook_13.m
format compact
% Initialize a matrix
matrix_1 = [4 6 2; 6 3 2]
% Get the number of values in a row
num_in_a_row = length(matrix_1)
% Get the total number of values in a matrix
num_of_vals = numel(matrix_1)
% Size of matrix (num rows num cols)
matrix_size = size(matrix_1)
[num_of_rows, num_of_cols] = size(matrix_1)
% Generate a random matrix with values between 20 and 30
% Matrix has two rows.
matrix_2 = randi([20,30],2)
% Modify a value inside a matrix (row 1, column 2)
% Remember matrices start at 1
matrix_2(1, 2) = 33
% Modify all row values in the first row
matrix_2(1,:) = 26
% Modify all column values in the first column
matrix_2(:,1) = 95
% Get the first value in the last row
first_val_last_row = matrix_2(end, 1)
% Get the second value in the last column
second_val_last_col = matrix_2(2, end)
% Delete the second column
matrix_2(:,2) = [];
Loops
For loops
edit matlab_cookbook_14.m
format compact
% Loop from 1 through 5
for i = 1:5
disp(i) % Display
end
% Add a space
disp(' ')
% Decrement from 5 to 0 in steps of 1
for i = 5:-1:0
disp(i)
end
% Add a space
disp(' ')
% Loop from 1 through 3
for i = [1 2 3]
disp(i)
end
% Add a space
disp(' ')
% Create a matrix
matrix_1 = [1 4 5; 6 2 7];
% Nested for loop to run through all values in a matrix
for row = 1:2
for col = 1:3
disp(matrix_1(row, col))
end
end
% Go through an entire vector
vector_1 = [2 8 3 5]
for i = 1:length(vector_1)
disp(vector_1(i))
end
Output:

While loops
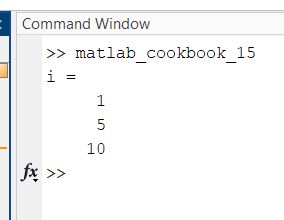
edit matlab_cookbook_15.m
format compact
% Create a while loop
i = 1
while i < 25
% If the number is divisible by 5
if(mod(i,5)) == 0
disp(i)
i = i + 1;
continue
end
% Else
i = i + 1;
if i >= 14
% Prematurely leave the while loop
break
end
end
Output:
Matrix Operations
edit matlab_cookbook_16.m
Here is the first part of the output.
format compact
% Initialize a 3x3 matrix
matrix_1 = [4 6 2; 3 6 14; 5 2 9]
matrix_2 = [2:4; 7:9]
matrix_3 = [5:7; 9:11]
matrix_4 = [1:2; 3:4; 2:3]
% Add two matrices together
matrix_2 + matrix_3
% Multiply corresponding elements of two matrices together
matrix_2 .* matrix_3
% Multiply two matrices together
matrix_2 * matrix_4
% Perform the square root on every value in a matrix
sqrt(matrix_1)
% Double everything in a matrix
matrix_2 = matrix_2 * 2
% Sum everything in each column
sum(matrix_2)
% Convert a matrix to a boolean array
% Any value greater than 5 is 1
greater_than_five = matrix_1 > 5
Cell Arrays
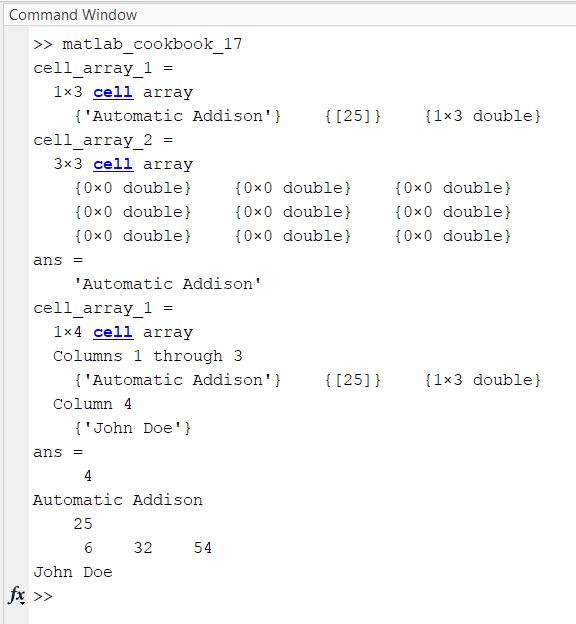
edit matlab_cookbook_17.m
format compact
% Create a cell array
cell_array_1 = {'Automatic Addison', 25, [6 32 54]}
% Preallocate a cell array to which we will later assign data
cell_array_2 = cell(3)
% Get the first value in the cell array
cell_array_1{1}
% Add more information
cell_array_1{4} = 'John Doe'
% Get the length of the cell array
length(cell_array_1)
% Display the values in a cell array
for i = 1:length(cell_array_1)
disp(cell_array_1{i})
end
Here is the output:
Strings
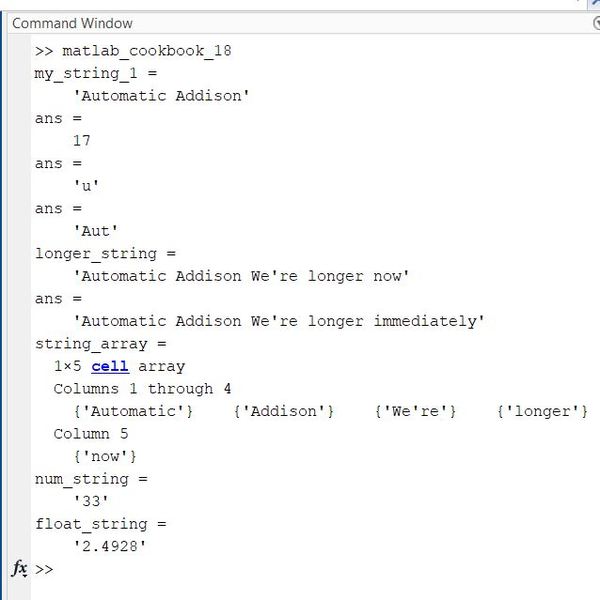
edit matlab_cookbook_18.m
format compact
% Initialize a string
my_string_1 = 'Automatic Addison'
% Get the length of the string
length(my_string_1)
% Get the second value in the string
my_string_1(2)
% Get the first three letters of the string
my_string_1(1:3)
% Concatenate
longer_string = strcat(my_string_1, ' We''re longer now')
% Replace a value in a string
strrep(longer_string, 'now', 'immediately')
% Split a string based on space delimiter
string_array = strsplit(longer_string, ' ')
% Convert an integer to a string
num_string = int2str(33)
% Convert a float to a string
float_string = num2str(2.4928)
Here is the output:
Structures
Here is how to create your own custom data type using structures. Structures consist of key-value pairs (like a dictionary).
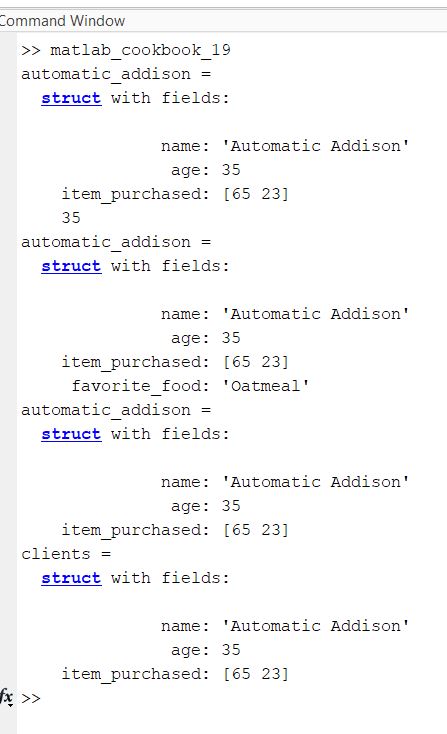
edit matlab_cookbook_19.m
format compact
automatic_addison = struct('name', 'Automatic Addison', ...
'age', 35, 'item_purchased', [65 23])
% Get his age
disp(automatic_addison.age)
% Add a field
automatic_addison.favorite_food = 'Oatmeal'
% Remove a field
automatic_addison = rmfield(automatic_addison, 'favorite_food')
% Store a structure in a vector
clients(1) = automatic_addison
Here is the output:
Tables
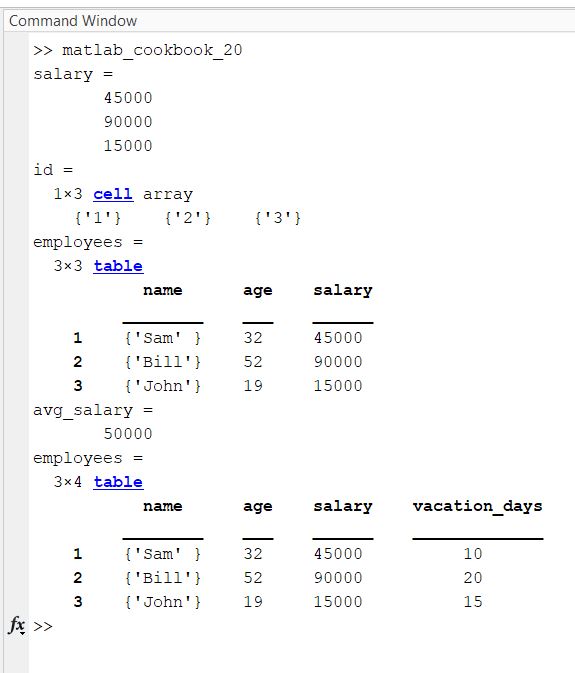
edit matlab_cookbook_20.m
format compact
name = {'Sam'; 'Bill'; 'John'};
age = [32; 52; 19];
salary = [45000; 90000; 15000]
id = {'1', '2', '3'}
% The name of each row will be the id
employees = table(name, age, salary, ...
'RowName', id)
% Get the average salary
avg_salary = mean(employees.salary)
% 'help table' command helps you find what you can do with tables
% Add a new field
employees.vacation_days = [10; 20; 15]
Here is the output:
File Input/Output
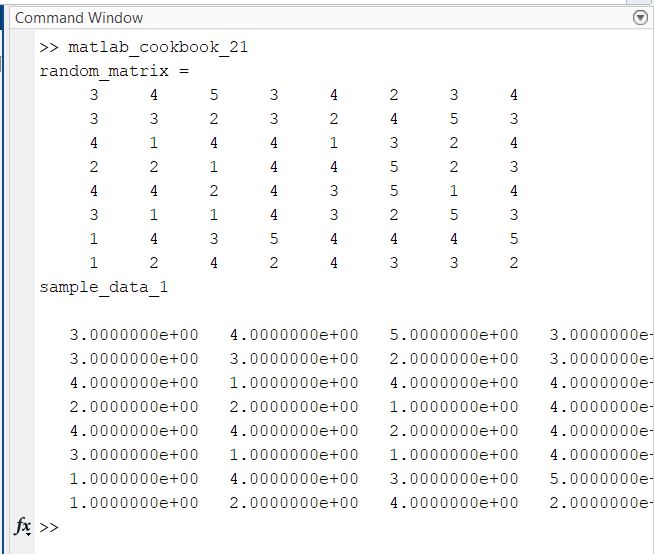
edit matlab_cookbook_21.m
format compact
% Generate a random 8x8 matrix
random_matrix = randi([1,5],8)
% Save the matrix as a text file
save sample_data_1.txt random_matrix -ascii
% Load the text file
load sample_data_1.txt
disp sample_data_1
type sample_data_1.txt
Here is the output:
Functions
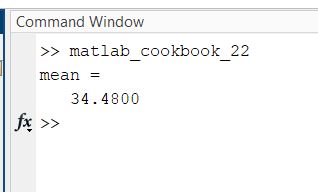
edit matlab_cookbook_22.m
format compact
% Input vector
values = [9.7, 63.5, 25.2, 72.9, 1.1];
% Calculate the average and store it
mean = average(values)
% Define a function named average.m that
% accepts an input vector and returns the average
function ave = average(x)
% Take the sum of all elements in x and divide
% by the number of elements
ave = sum(x(:))/numel(x);
end
Here is the output:
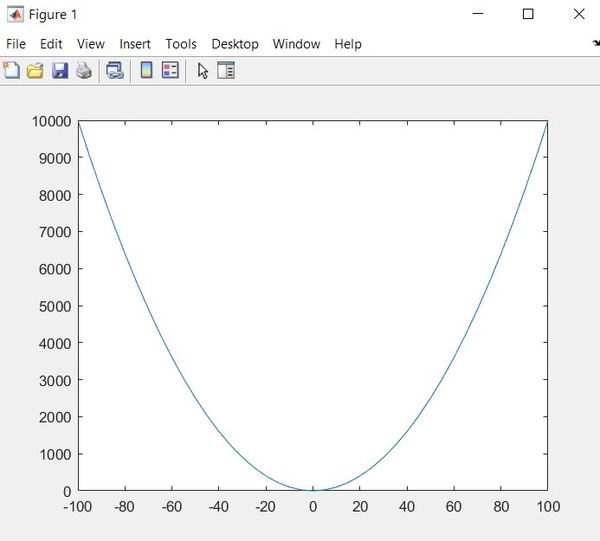
Creating a Plot
edit basic_plot.m
% Graph a parabola
x = [-100:5:100];
y = x.^2;
plot(x, y)
Here is the output: