How to Run a C++ Node
Ok, now that we have built our nodes, let’s run them.
Open up a new terminal window and launch the ROS Master.
roscore
In a new terminal tab, type the following command to run the publisher node:
rosrun noetic_basics_part_1 simple_publisher_node
Here is the output:
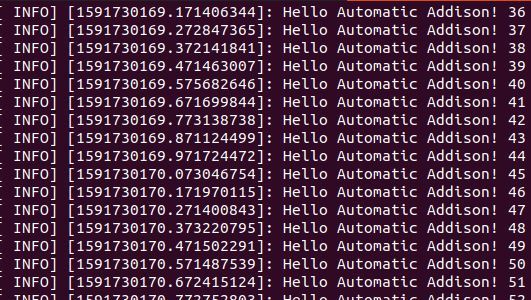
Now, let’s run the subscriber node. Type the following command in a new terminal tab.
rosrun noetic_basics_part_1 simple_subscriber_node
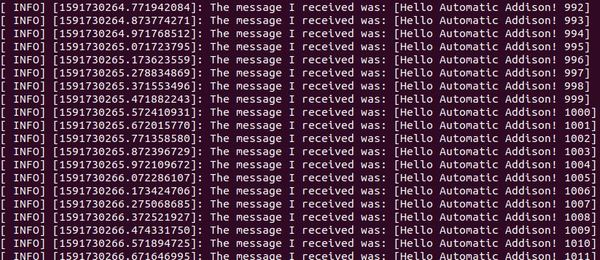
You’ll notice that the syntax for running a node in ROS is:
rosrun package-name executable-name
In a new terminal tab, check to see which nodes are running.
rosnode list
The /rosout node is a special node that starts up automatically when you launch the ROS Master. It is responsible for managing ROS-specific output messages to the terminal window.
If you want to find out information about the publisher node, you can type:
rosnode info /simple_publisher_node
That command aboves gives you a full account of what the node is all about. To find out more information about the subscriber node, type:
rosnode info /simple_subscriber_node
There are a bunch of commands for ROS nodes.
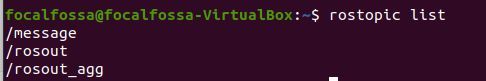
To list all active topics, type:
rostopic list
You can see the /message topic is currently active.
Now try these commands, and see what you get:
rostopic info message
rostopic type /message
rostopic bw /message
You can find out what all these commands mean at the ROS website here.
To visualize the publish-subscribe relationships between the nodes, type the following command:
rqt graph
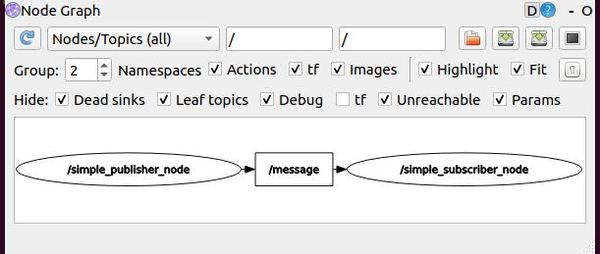
An incoming arrow indicates that a node subscribed to the topic. An outgoing arrow indicates that a node publishes to the topic.
You can close all terminal windows when you’re ready by pressing CTRL + C on your keyboard on each window.
How to Run a Python Node
In a new terminal window, launch ROS.
roscore
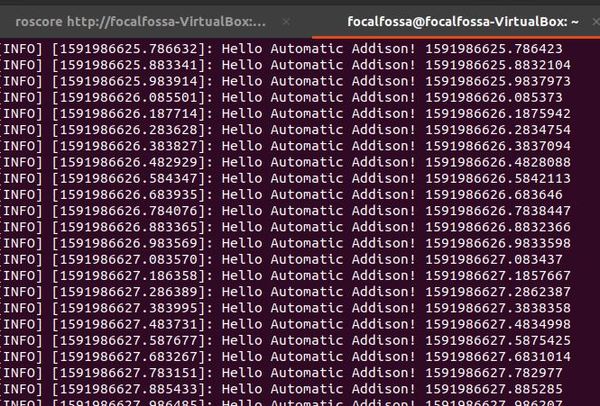
Open a new terminal window, and execute simple_python_publisher.py.
rosrun noetic_basics_part_1 simple_python_publisher.py
Here is the output:
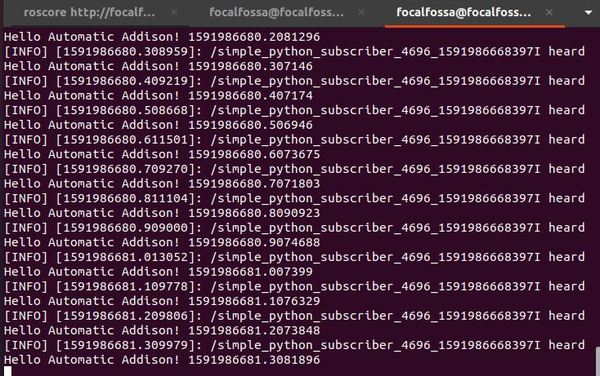
Open another terminal window and type:
rosrun noetic_basics_part_1 simple_python_subscriber.py
To stop the program, type CTRL+C in all terminal windows.

