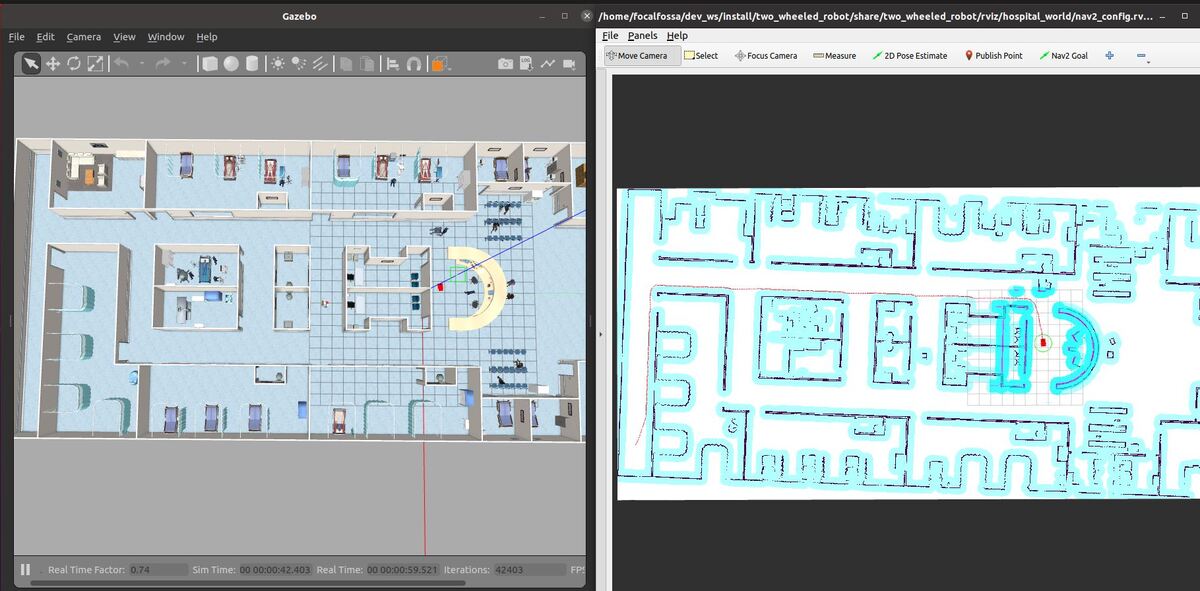
In this tutorial, I will show you how to go to a goal location when the battery of a simulated robot gets low. We will work with the BatteryState message provided by ROS.
The use case for this application is autonomous docking to a charging station.
Prerequisites
- You have completed this post.
You can find the files for this post here on my Google Drive.
Directions
Open a terminal window, and move to your package.
cd ~/dev_ws/src/two_wheeled_robot/scripts
Open a new script called navigate_to_charging_dock.py.
gedit navigate_to_charging_dock.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3
"""
Description:
Navigate to a charging dock once the battery gets low.
-------
Subscription Topics:
Current battery state
/battery_status - sensor_msgs/BatteryState
-------
Publishing Topics:
Velocity command to navigate to the charging dock.
/cmd_vel - geometry_msgs/Twist
-------
Author: Addison Sears-Collins
Website: AutomaticAddison.com
Date: November 16, 2021
"""
import time # Time library
from rclpy.duration import Duration # Handles time for ROS 2
import rclpy # Python client library for ROS 2
from rclpy.node import Node # Handles the creation of nodes
from rclpy.executors import MultiThreadedExecutor
from robot_navigator import BasicNavigator, NavigationResult # Helper module
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped # Pose with ref frame and timestamp
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist # Velocity command
from sensor_msgs.msg import BatteryState # Battery status
# Holds the current state of the battery
this_battery_state = BatteryState()
prev_battery_state = BatteryState()
# Flag for detecting the change in the battery state
low_battery = False
low_battery_min_threshold = 0.25
class ConnectToChargingDockNavigator(Node):
"""
Navigates and connects to the charging dock
"""
def __init__(self):
# Initialize the class using the constructor
super().__init__('connect_to_charging_dock_navigator')
# Create a publisher
# This node publishes the desired linear and angular velocity of the robot
self.publisher_cmd_vel = self.create_publisher(
Twist,
'/cmd_vel',
10)
timer_period = 0.1
self.timer = self.create_timer(timer_period, self.navigate_to_dock)
# Declare velocities
self.linear_velocity = 0.0
self.angular_velocity = 0.15
def navigate_to_dock(self):
global low_battery
if low_battery == False:
return None
self.get_logger().info('Navigating to the charging dock...')
# Launch the ROS 2 Navigation Stack
navigator = BasicNavigator()
# Wait for navigation to fully activate. Use this line if autostart is set to true.
navigator.waitUntilNav2Active()
# If desired, you can change or load the map as well
# navigator.changeMap('/path/to/map.yaml')
# You may use the navigator to clear or obtain costmaps
# navigator.clearAllCostmaps() # also have clearLocalCostmap() and clearGlobalCostmap()
# global_costmap = navigator.getGlobalCostmap()
# local_costmap = navigator.getLocalCostmap()
# Set the robot's goal pose
goal_pose = PoseStamped()
goal_pose.header.frame_id = 'map'
goal_pose.header.stamp = navigator.get_clock().now().to_msg()
goal_pose.pose.position.x = 0.0
goal_pose.pose.position.y = 2.0
goal_pose.pose.position.z = 0.25
goal_pose.pose.orientation.x = 0.0
goal_pose.pose.orientation.y = 0.0
goal_pose.pose.orientation.z = 0.0
goal_pose.pose.orientation.w = 1.0
# Go to the goal pose
navigator.goToPose(goal_pose)
i = 0
# Keep doing stuff as long as the robot is moving towards the goal
while not navigator.isNavComplete():
# Do something with the feedback
i = i + 1
feedback = navigator.getFeedback()
if feedback and i % 5 == 0:
print('Distance remaining: ' + '{:.2f}'.format(
feedback.distance_remaining) + ' meters.')
# Some navigation timeout to demo cancellation
if Duration.from_msg(feedback.navigation_time) > Duration(seconds=600.0):
navigator.cancelNav()
# Do something depending on the return code
result = navigator.getResult()
if result == NavigationResult.SUCCEEDED:
print('Successfully reached charging dock staging area...')
low_battery = False
self.connect_to_dock()
elif result == NavigationResult.CANCELED:
print('Goal was canceled!')
elif result == NavigationResult.FAILED:
print('Goal failed!')
else:
print('Goal has an invalid return status!')
def connect_to_dock(self):
# While the battery is not charging
while this_battery_state.power_supply_status != 1:
# Publish the current battery state
self.get_logger().info('NOT CHARGING...')
# Send the velocity command to the robot by publishing to the topic
cmd_vel_msg = Twist()
cmd_vel_msg.linear.x = self.linear_velocity
cmd_vel_msg.angular.z = self.angular_velocity
self.publisher_cmd_vel.publish(cmd_vel_msg)
time.sleep(0.1)
# Stop the robot
cmd_vel_msg = Twist()
cmd_vel_msg.linear.x = 0.0
cmd_vel_msg.angular.z = 0.0
self.publisher_cmd_vel.publish(cmd_vel_msg)
self.get_logger().info('CHARGING...')
self.get_logger().info('Successfully connected to the charging dock!')
class BatteryStateSubscriber(Node):
"""
Subscriber node to the current battery state
"""
def __init__(self):
# Initialize the class using the constructor
super().__init__('battery_state_subscriber')
# Create a subscriber
# This node subscribes to messages of type
# sensor_msgs/BatteryState
self.subscription_battery_state = self.create_subscription(
BatteryState,
'/battery_status',
self.get_battery_state,
10)
def get_battery_state(self, msg):
"""
Update the current battery state.
"""
global this_battery_state
global prev_battery_state
global low_battery
prev_battery_state = this_battery_state
this_battery_state = msg
# Check for low battery
if prev_battery_state.percentage >= low_battery_min_threshold and this_battery_state.percentage < low_battery_min_threshold:
low_battery = True
def main(args=None):
"""
Entry point for the program.
"""
# Initialize the rclpy library
rclpy.init(args=args)
try:
# Create the nodes
connect_to_charging_dock_navigator = ConnectToChargingDockNavigator()
battery_state_subscriber = BatteryStateSubscriber()
# Set up mulithreading
executor = MultiThreadedExecutor(num_threads=4)
executor.add_node(connect_to_charging_dock_navigator)
executor.add_node(battery_state_subscriber)
try:
# Spin the nodes to execute the callbacks
executor.spin()
finally:
# Shutdown the nodes
executor.shutdown()
connect_to_charging_dock_navigator.destroy_node()
battery_state_subscriber.destroy_node()
finally:
# Shutdown
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Save the file and close it.
Add the script to your CMakeLists.txt file.
cd ~/dev_ws/src/two_wheeled_robot/
gedit CMakeLists.txt
Save and close the file.
Update the parameters.
cd ~/dev_ws/src/two_wheeled_robot/params/hospital_world/
gedit nav2_connect_to_charging_dock_params.yaml
Save and close the file.
Add the node to your launch file.
cd ~/dev_ws/src/two_wheeled_robot/launch/hospital_world/
Add the hospital_world_connect_to_charging_dock.launch.py file from this folder.
# Author: Addison Sears-Collins
# Date: November 16, 2021
# Description: Launch a two-wheeled robot using the ROS 2 Navigation Stack.
# The spawning of the robot is performed by the Gazebo-ROS spawn_entity node.
# The robot must be in both SDF and URDF format.
# If you want to spawn the robot in a pose other than the default, be sure to set that inside
# the nav2_params_path yaml file: amcl ---> initial_pose: [x, y, z, yaw]
# The robot will return to the charging dock when the /battery_status percentage is low.
# https://automaticaddison.com
import os
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument, IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.conditions import IfCondition, UnlessCondition
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch.substitutions import Command, LaunchConfiguration, PythonExpression
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch_ros.substitutions import FindPackageShare
def generate_launch_description():
package_name = 'two_wheeled_robot'
robot_name_in_model = 'two_wheeled_robot'
default_launch_dir = 'launch'
gazebo_models_path = 'models'
map_file_path = 'maps/hospital_world/hospital_world.yaml'
nav2_params_path = 'params/hospital_world/nav2_connect_to_charging_dock_params.yaml'
robot_localization_file_path = 'config/ekf.yaml'
rviz_config_file_path = 'rviz/hospital_world/nav2_config.rviz'
sdf_model_path = 'models/two_wheeled_robot_description/model.sdf'
urdf_file_path = 'urdf/two_wheeled_robot.urdf'
world_file_path = 'worlds/hospital.world'
nav_to_charging_dock_script = 'navigate_to_charging_dock.py'
# Pose where we want to spawn the robot
spawn_x_val = '0.0'
spawn_y_val = '2.0'
spawn_z_val = '0.25'
spawn_yaw_val = '0.0'
########## You do not need to change anything below this line ###############
# Set the path to different files and folders.
pkg_gazebo_ros = FindPackageShare(package='gazebo_ros').find('gazebo_ros')
pkg_share = FindPackageShare(package=package_name).find(package_name)
default_launch_dir = os.path.join(pkg_share, default_launch_dir)
default_urdf_model_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, urdf_file_path)
robot_localization_file_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, robot_localization_file_path)
default_rviz_config_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, rviz_config_file_path)
world_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, world_file_path)
gazebo_models_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, gazebo_models_path)
os.environ["GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH"] = gazebo_models_path
nav2_dir = FindPackageShare(package='nav2_bringup').find('nav2_bringup')
nav2_launch_dir = os.path.join(nav2_dir, 'launch')
sdf_model_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, sdf_model_path)
static_map_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, map_file_path)
nav2_params_path = os.path.join(pkg_share, nav2_params_path)
nav2_bt_path = FindPackageShare(package='nav2_bt_navigator').find('nav2_bt_navigator')
# Launch configuration variables specific to simulation
autostart = LaunchConfiguration('autostart')
headless = LaunchConfiguration('headless')
map_yaml_file = LaunchConfiguration('map')
namespace = LaunchConfiguration('namespace')
params_file = LaunchConfiguration('params_file')
rviz_config_file = LaunchConfiguration('rviz_config_file')
sdf_model = LaunchConfiguration('sdf_model')
slam = LaunchConfiguration('slam')
urdf_model = LaunchConfiguration('urdf_model')
use_namespace = LaunchConfiguration('use_namespace')
use_robot_state_pub = LaunchConfiguration('use_robot_state_pub')
use_rviz = LaunchConfiguration('use_rviz')
use_sim_time = LaunchConfiguration('use_sim_time')
use_simulator = LaunchConfiguration('use_simulator')
world = LaunchConfiguration('world')
# Map fully qualified names to relative ones so the node's namespace can be prepended.
# In case of the transforms (tf), currently, there doesn't seem to be a better alternative
# https://github.com/ros/geometry2/issues/32
# https://github.com/ros/robot_state_publisher/pull/30
# TODO(orduno) Substitute with `PushNodeRemapping`
# https://github.com/ros2/launch_ros/issues/56
remappings = [('/tf', 'tf'),
('/tf_static', 'tf_static')]
# Declare the launch arguments
declare_namespace_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='namespace',
default_value='',
description='Top-level namespace')
declare_use_namespace_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='use_namespace',
default_value='false',
description='Whether to apply a namespace to the navigation stack')
declare_autostart_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='autostart',
default_value='true',
description='Automatically startup the nav2 stack')
declare_map_yaml_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='map',
default_value=static_map_path,
description='Full path to map file to load')
declare_params_file_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='params_file',
default_value=nav2_params_path,
description='Full path to the ROS2 parameters file to use for all launched nodes')
declare_rviz_config_file_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='rviz_config_file',
default_value=default_rviz_config_path,
description='Full path to the RVIZ config file to use')
declare_sdf_model_path_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='sdf_model',
default_value=sdf_model_path,
description='Absolute path to robot sdf file')
declare_simulator_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='headless',
default_value='False',
description='Whether to execute gzclient')
declare_slam_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='slam',
default_value='False',
description='Whether to run SLAM')
declare_urdf_model_path_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='urdf_model',
default_value=default_urdf_model_path,
description='Absolute path to robot urdf file')
declare_use_robot_state_pub_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='use_robot_state_pub',
default_value='True',
description='Whether to start the robot state publisher')
declare_use_rviz_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='use_rviz',
default_value='True',
description='Whether to start RVIZ')
declare_use_sim_time_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='use_sim_time',
default_value='true',
description='Use simulation (Gazebo) clock if true')
declare_use_simulator_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='use_simulator',
default_value='True',
description='Whether to start the simulator')
declare_world_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
name='world',
default_value=world_path,
description='Full path to the world model file to load')
# Specify the actions
# Start Gazebo server
start_gazebo_server_cmd = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(os.path.join(pkg_gazebo_ros, 'launch', 'gzserver.launch.py')),
condition=IfCondition(use_simulator),
launch_arguments={'world': world}.items())
# Start Gazebo client
start_gazebo_client_cmd = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(os.path.join(pkg_gazebo_ros, 'launch', 'gzclient.launch.py')),
condition=IfCondition(PythonExpression([use_simulator, ' and not ', headless])))
# Launch the robot
spawn_entity_cmd = Node(
package='gazebo_ros',
executable='spawn_entity.py',
arguments=['-entity', robot_name_in_model,
'-file', sdf_model,
'-x', spawn_x_val,
'-y', spawn_y_val,
'-z', spawn_z_val,
'-Y', spawn_yaw_val],
output='screen')
# Start robot localization using an Extended Kalman filter
start_robot_localization_cmd = Node(
package='robot_localization',
executable='ekf_node',
name='ekf_filter_node',
output='screen',
parameters=[robot_localization_file_path,
{'use_sim_time': use_sim_time}])
# Subscribe to the joint states of the robot, and publish the 3D pose of each link.
start_robot_state_publisher_cmd = Node(
condition=IfCondition(use_robot_state_pub),
package='robot_state_publisher',
executable='robot_state_publisher',
namespace=namespace,
parameters=[{'use_sim_time': use_sim_time,
'robot_description': Command(['xacro ', urdf_model])}],
remappings=remappings,
arguments=[default_urdf_model_path])
# Launch RViz
start_rviz_cmd = Node(
condition=IfCondition(use_rviz),
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
name='rviz2',
output='screen',
arguments=['-d', rviz_config_file])
# Launch navigation to the charging dock
start_navigate_to_charging_dock_cmd = Node(
package=package_name,
executable=nav_to_charging_dock_script)
# Launch the ROS 2 Navigation Stack
start_ros2_navigation_cmd = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(os.path.join(nav2_launch_dir, 'bringup_launch.py')),
launch_arguments = {'namespace': namespace,
'use_namespace': use_namespace,
'slam': slam,
'map': map_yaml_file,
'use_sim_time': use_sim_time,
'params_file': params_file,
'autostart': autostart}.items())
# Create the launch description and populate
ld = LaunchDescription()
# Declare the launch options
ld.add_action(declare_namespace_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_namespace_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_autostart_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_map_yaml_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_params_file_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_rviz_config_file_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_sdf_model_path_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_simulator_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_slam_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_urdf_model_path_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_robot_state_pub_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_rviz_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_sim_time_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_simulator_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_world_cmd)
# Add any actions
ld.add_action(start_gazebo_server_cmd)
ld.add_action(start_gazebo_client_cmd)
#ld.add_action(spawn_entity_cmd)
ld.add_action(start_robot_localization_cmd)
ld.add_action(start_robot_state_publisher_cmd)
ld.add_action(start_rviz_cmd)
ld.add_action(start_navigate_to_charging_dock_cmd)
ld.add_action(start_ros2_navigation_cmd)
return ld
Launch the Launch File
We will now build our package.
cd ~/dev_ws/
colcon build
Open a new terminal window, and run the following message to indicate the battery is at full charge.
ros2 topic pub /battery_status sensor_msgs/BatteryState '{voltage: 9.0, percentage: 1.0, power_supply_status: 3}'
Open a new terminal and launch the robot.
ros2 launch two_wheeled_robot hospital_world_connect_to_charging_dock.launch.py
Select the Nav2 Goal button at the top of RViz and click somewhere on the map to command the robot to navigate to any reachable goal location.
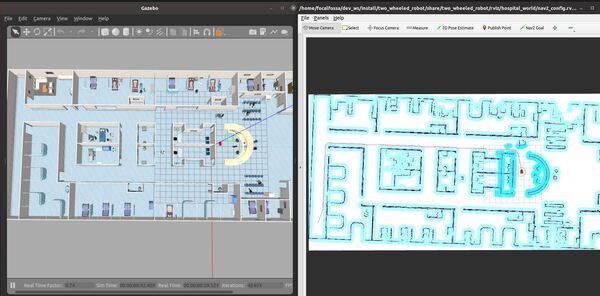
The robot will move to the goal location.
While the robot is moving, stop the /battery_status publisher.
CTRL + C
Now run this command to indicate low battery:
ros2 topic pub /battery_status sensor_msgs/BatteryState '{voltage: 2.16, percentage: 0.24, power_supply_status: 3}'
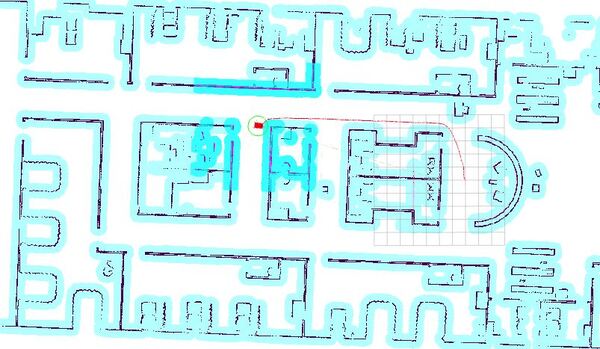
The robot will plan a path to the staging area and then move along that path.
Once the robot reaches the staging area, the robot will spin indefinitely. This spin, in a real-world application, would be navigating to a charging dock with the appropriate algorithm (using an infrared sensor, ARTag, AprilTag, etc.).
Let’s assume the robot has now reached the charging dock and is charging.
Press CTRL + C to stop the /battery_status publisher, and type:
ros2 topic pub /battery_status sensor_msgs/BatteryState '{voltage: 2.16, percentage: 0.24, power_supply_status: 1}'
That 1 for the power_supply_status indicates the battery is CHARGING.
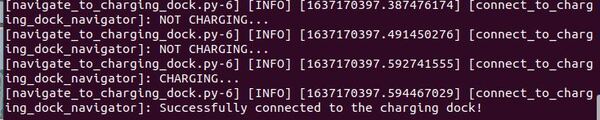
That’s it! Keep building!